That advice, more popularly known as the “success sequence,” is often credited to research done by Brookings Institution scholars Isabel Sawhill and Ron Haskins, though others have made similar observations. In his recent book, “Agency,” Ian Rowe of the American Enterprise Institute writes that the message “has attracted many admirers because of the simplicity of the three steps that young people, even if born into disadvantaged circumstances or raised by a young single parent, can themselves control and take in their lives.”
The effort nevertheless faced significant backlash from detractors who accused then-Mayor Michael Bloomberg of stigmatizing teen pregnancy and pushing a “moralistic, conservative agenda to revitalize marriage,” Mr. Rowe writes. Mr. Bloomberg’s successor, Bill de Blasio, ultimately abandoned the effort. Public moralizing has since fallen further out of favor and been replaced by a kind of self-congratulatory nonjudgmentalism. In today’s New York, you’re likely to see ads for free syringes and directions to “safe” injections sites for junkies, even as drug overdoses have reached record levels.
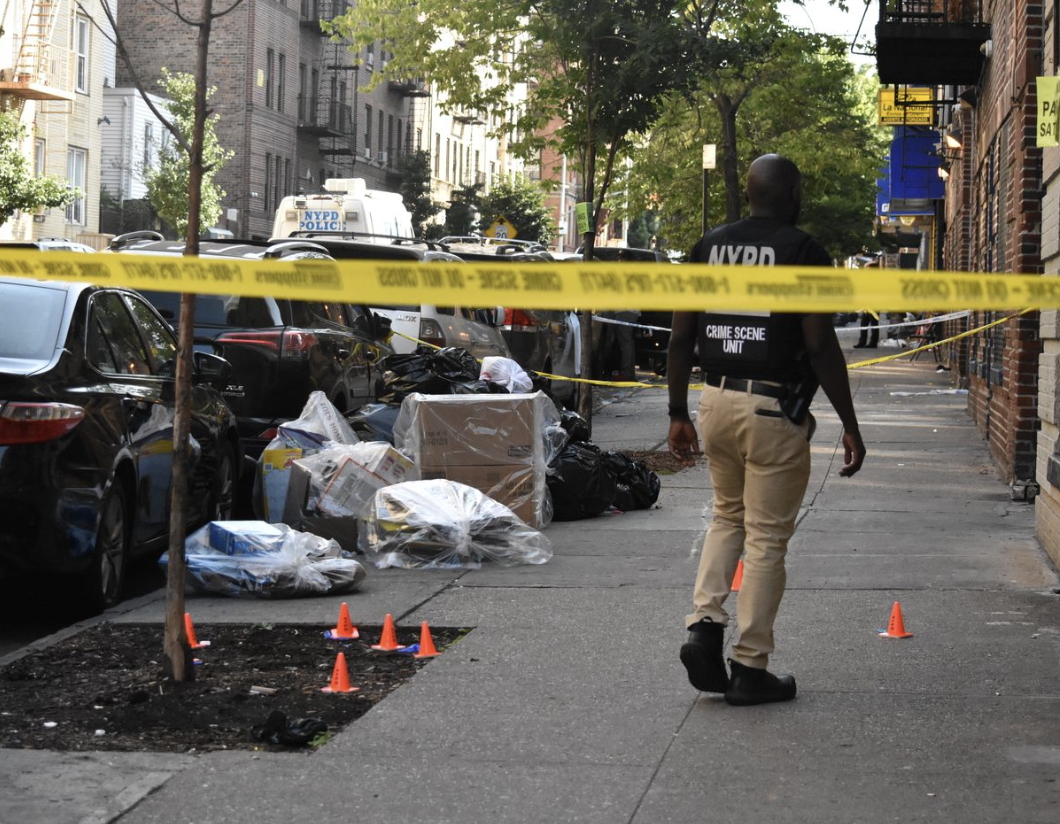
We could use more of that moralizing from public officials, whether the issue is solo parenting, substance abuse or crime. The success sequence works to keep people not only off the dole but also out of trouble with the law. High-school graduates and children raised by both parents are much less likely to end up in jail. “Virtually every major social pathology,” political scientist Stephen Baskervillewrites, “has been linked to fatherless children: violent crime, drug and alcohol abuse, truancy, unwed pregnancy, suicide, and psychological disorders—all correlating more strongly with fatherlessness than with any other single factor, surpassing even race and poverty.”
America’s crime debate tends to focus on so-called root causes, such as joblessness. But it’s worth remembering that the sharpest increase in violent crime began in the 1960s, a decade that saw low unemployment, strong economic growth and a doubling of black household incomes. As notable, labor-force participation rates of young black men fell during the 1980s and ’90s, one of the longest periods of sustained economic growth in U.S. history.
A new academic paper from the Institute for Family Studies doesn’t deny that economic conditions play a role in criminal behavior. And co-authors Rafael Mangual, Brad Wilcox, Joseph Price and Seth Cannon write that “changes in law-enforcement and the prosecution of criminals have also had a hand in the recent uptick in violent crime in American cities.” The paper’s main argument, however, is that family instability may be the biggest factor of all and that it’s not receiving the attention it deserves.
“Cities are safer when two-parent families are dominant and more crime-ridden when family instability is common,” the authors write. Nationwide, the total crime rate is about 48% higher in cities “that have above the median share of single-parent families, compared to cities that have fewer single-parent families.” Even when controlling for variables such as race, income and educational attainment, “the association between family structure and total crime rates, as well as violent crime rates, in cities across the United States remains statistically significant.”
Having a father around, the authors note, is about more than an additional paycheck. Fathers teach their sons responsibility, self-control, how to carry themselves, how to treat women. They tend to be more effective disciplinarians, and their involvement in childrearing is linked to positive outcomes in the academic development of their children, “especially in mathematics and verbal skills.” That finding “has been established for both sons and daughters but, unsurprisingly, it is especially pronounced among boys. The presence of married fathers is also protective against school suspensions and expulsions, as well as the risk of dropping out of high school.”
Between 1960 and 2019, the percentage of babies in the U.S. born to unwed mothers grew from 5% to almost 50%. “Shifts from the late-1960s to the 1990s away from stable families have left some cities, and especially some neighborhoods, vulnerable to higher rates of crime, especially violent crime,” the study concludes. “We need to realign material and cultural incentives in our cities to favor marriage and stable families, not undercut them.”
We all know single mothers—some of us even may be related to them—who heroically beat these odds and raised children that have gone on to lead productive lives. The public-policy goal should be to reduce the number of people who will have to face those odds. And that means calling out behavior that is objectively harmful to people and society in general.
To see this article in its entirety and to subscribe to others like it, please choose to read more.
Source: The Biggest Root Cause of Crime Is Fatherlessness – WSJ
 Listen Online
Listen Online Watch Online
Watch Online Find a Station in Your Area
Find a Station in Your Area








 Listen Now
Listen Now Watch Online
Watch Online
