By: David Brooks – nytimes.com – January 1, 2018
Imagine three kids running around a maypole, forming a chain with their arms. The innermost kid is holding the pole with one hand. The faster they run, the more centrifugal force there is tearing the chain apart. The tighter they grip, the more centripetal force there is holding the chain together. Eventually centrifugal force exceeds centripetal force and the chain breaks.
That’s essentially what is happening in this country, N.Y.U.’s Jonathan Haidt argued in a lecture delivered to the Manhattan Institute in November. He listed some of the reasons centrifugal forces may now exceed centripetal: the loss of the common enemies we had in World War II and the Cold War, an increasingly fragmented media, the radicalization of the Republican Party, and a new form of identity politics, especially on campus.
Haidt made the interesting point that identity politics per se is not the problem. Identity politics is just political mobilization around group characteristics. The problem is that identity politics has dropped its centripetal elements and become entirely centrifugal.
Martin Luther King described segregation and injustice as forces tearing us apart. He appealed to universal principles and our common humanity as ways to heal prejudice and unite the nation. He appealed to common religious principles, the creed of our founding fathers and a common language of love to drive out prejudice. King “framed our greatest moral failing as an opportunity for centripetal redemption,” Haidt observed.
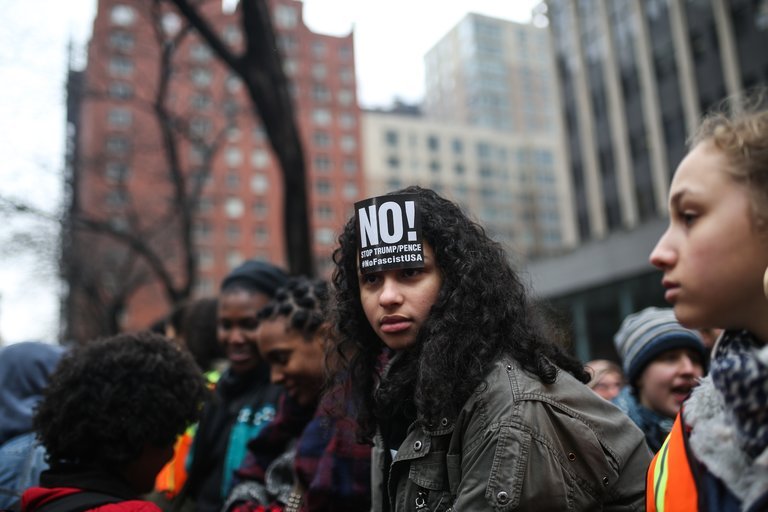
From an identity politics that emphasized our common humanity, we’ve gone to an identity politics that emphasizes having a common enemy. On campus these days, current events are often depicted as pure power struggles — oppressors acting to preserve their privilege over the virtuous oppressed.
“A funny thing happens,” Haidt said, “when you take young human beings, whose minds evolved for tribal warfare and us/them thinking, and you fill those minds full of binary dimensions. You tell them that one side in each binary is good and the other is bad. You turn on their ancient tribal circuits, preparing them for battle. Many students find it thrilling; it floods them with a sense of meaning and purpose.”
The problem is that tribal common-enemy thinking tears a diverse nation apart.
This pattern is not just on campus. Look at the negative polarization that marks our politics. Parties, too, are no longer bound together by creeds but by enemies.
In 1994, only 16 percent of Democrats had a “very unfavorable” view of the G.O.P. Now, 38 percent do. Then, only 17 percent of Republicans had a “very unfavorable” view of Democrats. Now, 43 percent do. When the Pew Research Center asked Democrats and Republicans to talk about each other, they tended to use the same words: closed-minded, dishonest, immoral, lazy, unintelligent.
Furthermore, it won’t be easy to go back to the common-humanity form of politics. King was operating when there was high social trust. He could draw on a biblical metaphysic debated over 3,000 years. He could draw on an American civil religion that had been refined over 300 years.
Over the past two generations, however, excessive individualism and bad schooling have corroded both of those sources of cohesion.
In 1995, the French intellectual Pascal Bruckner published “The Temptation of Innocence,” in which he argued that excessive individualism paradoxically leads to in-group/out-group tribalism. Modern individualism releases each person from social obligation, but “being guided only by the lantern of his own understanding, the individual loses all assurance of a place, an order, a definition. He may have gained freedom, but he has lost security.”
In societies like ours, individuals are responsible for their own identity, happiness and success. “Everyone must sell himself as a person in order to be accepted,” Bruckner wrote. We all are constantly comparing ourselves to others and, of course, coming up short. The biggest anxiety is moral. We each have to write our own gospel that defines our own virtue.
The easiest way to do that is to tell a tribal oppressor/oppressed story and build your own innocence on your status as victim. Just about everybody can find a personal victim story. Once you’ve identified your herd’s oppressor — the neoliberal order, the media elite, white males, whatever — your goodness is secure. You have virtue without obligation. Nothing is your fault.
“What is moral order today? Not so much the reign of right-thinking people as that of right-suffering, the cult of everyday despair,” Bruckner continued. “I suffer, therefore I am worthy. … Suffering is analogous to baptism, a dubbing that inducts us into the order of a higher humanity, hoisting us above our peers.”
Haidt and Bruckner are very different writers, with different philosophies. But they both point to the fact that we’ve regressed from a sophisticated moral ethos to a primitive one. The crooked timber school of humanity says the line between good and evil runs through each person and we fight injustice on the basis of our common humanity. The oppressor/oppressed morality says the line runs between tribes. That makes it easy to feel good about yourself. But it makes you very hard to live with.
 Listen Online
Listen Online Watch Online
Watch Online Find a Station in Your Area
Find a Station in Your Area







 Listen Now
Listen Now Watch Online
Watch Online
